What to Eat and What to Avoid are common discussions in Maintaining a heart-healthy diet is one of the most effective strategies to reduce the risk of heart disease. But what exactly should you eat to protect your heart, and what should you avoid?
What Are Heart-Healthy Foods?
A heart-healthy diet focuses on patterns that promote cardiovascular well-being by positively affecting blood pressure, inflammation, cholesterol, and triglyceride levels. Key guidelines recommended:
- Maintaining a healthy weight by balancing calorie intake with physical activity.
- Eating a wide variety of fruits and vegetables.
- Opting for whole grains over refined grains.
- Using healthy plant oils like olive oil instead of tropical oils like palm oil.
- Choosing healthy protein sources like plant-based proteins, seafood, and lean meats.
- Minimizing added sugars and salt.
- Limiting alcohol intake.
- Choosing minimally processed foods.
Heart-Healthy Foods to Include
Here’s a closer look at some of the best foods to incorporate into your heart-healthy diet:
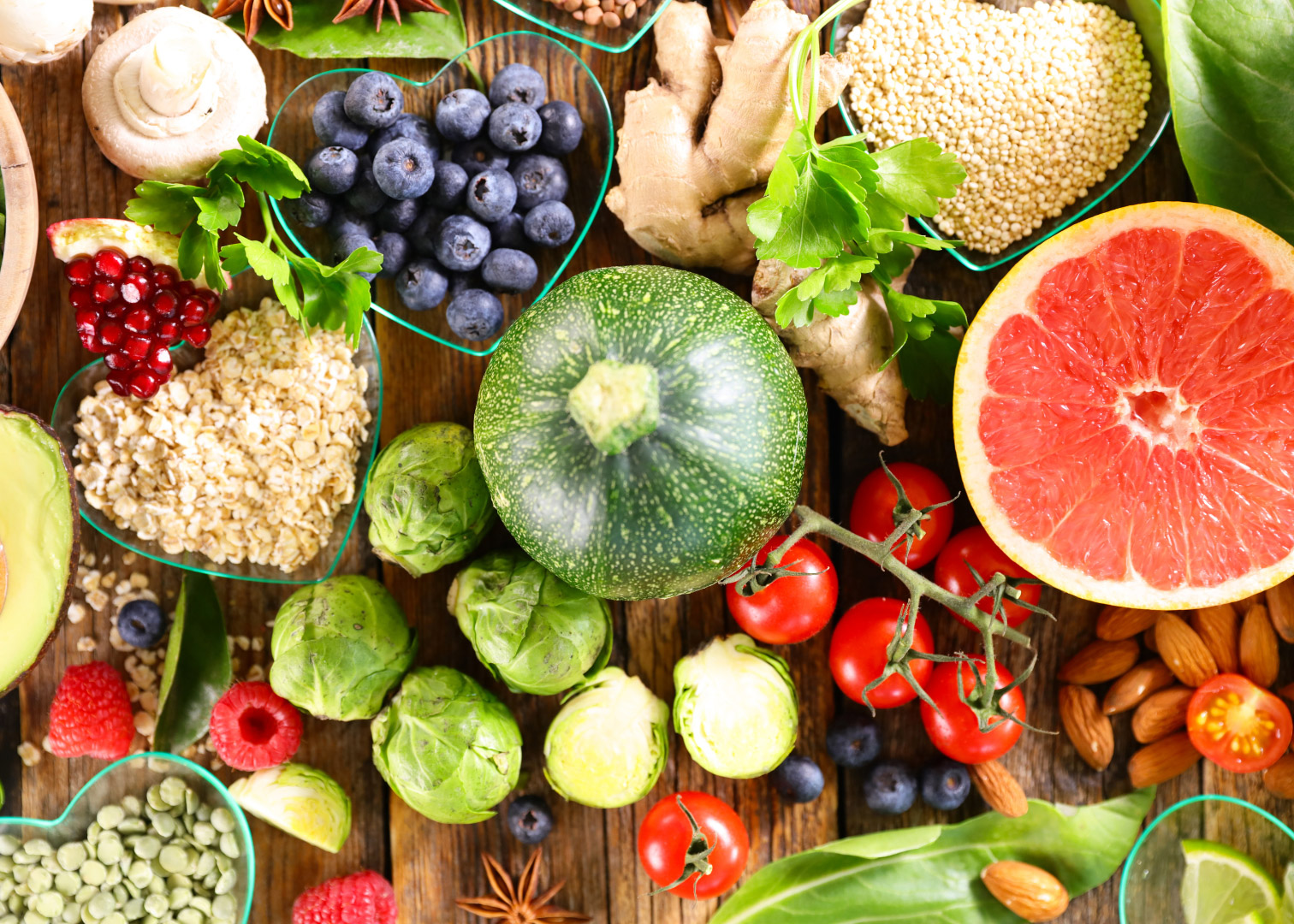
- Fruits and Vegetables: A diet rich in fruits and vegetables is linked to a lower risk of cardiovascular disease. They provide essential antioxidants that help protect the arteries. Strive to eat a variety of colors and types of vegetables, and include fruits like berries, apples, and oranges, which have been shown to reduce inflammation and oxidative stress linked to heart disease.
- Leafy greens like spinach and kale are rich in nitrates, which relax blood vessels and reduce blood pressure.
- Berries such as strawberries and blueberries are loaded with antioxidants, which can significantly improve heart health.
- Whole Grains: Whole grains, rich in fiber, are crucial for maintaining healthy cholesterol levels. Replacing refined grains with whole grains, such as brown rice, quinoa, oats, and whole-wheat products, lowers the risk of coronary heart disease.
- Healthy Proteins:
- Legumes (beans, lentils, chickpeas) are excellent sources of fiber and protein, helping reduce cholesterol and improve blood pressure.
- Nuts are rich in heart-healthy fats and can lower the risk of cardiovascular disease when consumed in moderation.
- Oily fish like salmon, mackerel, and sardines are packed with omega-3 fatty acids, known for their anti-inflammatory properties and ability to lower heart disease risk.
- Nonfat and Low-Fat Dairy: Switching to nonfat or low-fat dairy products can reduce the intake of saturated fats, promoting heart health. Some options include fat-free or low-fat milk, yogurt, and cheese.
- Unsaturated Fats and Oils: Unsaturated fats, found in foods like avocados, nuts, seeds, and healthy oils, can lower bad cholesterol levels and reduce inflammation. Opt for cooking oils such as olive oil and canola oil, which are high in monounsaturated and polyunsaturated fats.
- Foods to Avoid for Heart Health: While some foods boost heart health, others can be harmful. A diet high in sodium, saturated fat, added sugars, and processed foods can increase the risk of heart disease. According to some research it’s best to avoid:
- High-fat dairy products like whole milk and cream.
- Fatty and processed meats such as bacon, sausages, and deli meats.
- Tropical oils (coconut and palm oil) and partially hydrogenated fats.
- Sugary foods and beverages like soda and candy.
- Foods high in sodium, such as processed snacks and canned soups.
- Excessive alcohol consumption, which can raise blood pressure and contribute to heart disease.
Best Diets for Heart Disease PreventionIncorporating heart-healthy foods into your daily meals is essential for long-term cardiovascular health. Two diets, in particular, stand out for their heart health benefits:
- DASH Diet: The DASH (Dietary Approaches to Stop Hypertension) diet emphasizes fruits, vegetables, whole grains, lean proteins, and low-fat dairy. It limits foods high in saturated fats and sugar, making it an excellent choice for those looking to reduce blood pressure and improve heart health.
- Mediterranean Diet: Based on the eating habits of people in countries bordering the Mediterranean Sea, this plant-based diet focuses on vegetables, fruits, whole grains, legumes, and healthy fats like olive oil. It’s associated with a reduced risk of heart disease and other chronic conditions.
A heart-healthy diet doesn’t have to be complicated. By focusing on a balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, healthy proteins, and unsaturated fats, while avoiding processed and high-fat foods, you can significantly lower your risk of heart disease and enjoy a healthier, longer life.Remember, along with a nutritious diet, maintaining a healthy lifestyle that includes regular exercise, stress management, and sufficient sleep is key to optimizing your cardiovascular health.